Understanding the Future of Electric Charging Networks
Electric vehicles are taking the world by storm as more and more automobile manufacturers join the race to produce environmentally-friendly cars. However, while the majority of the focus has been on the vehicles themselves, another crucial aspect of this green revolution is often overlooked – the electric charging networks. As electric vehicles become more popular, the demand for efficient and accessible charging infrastructure will continue to rise. In this article, we will dive into the future of electric charging networks, exploring the current state of the industry, key challenges, and potential solutions to ensure a smooth transition to an all-electric future.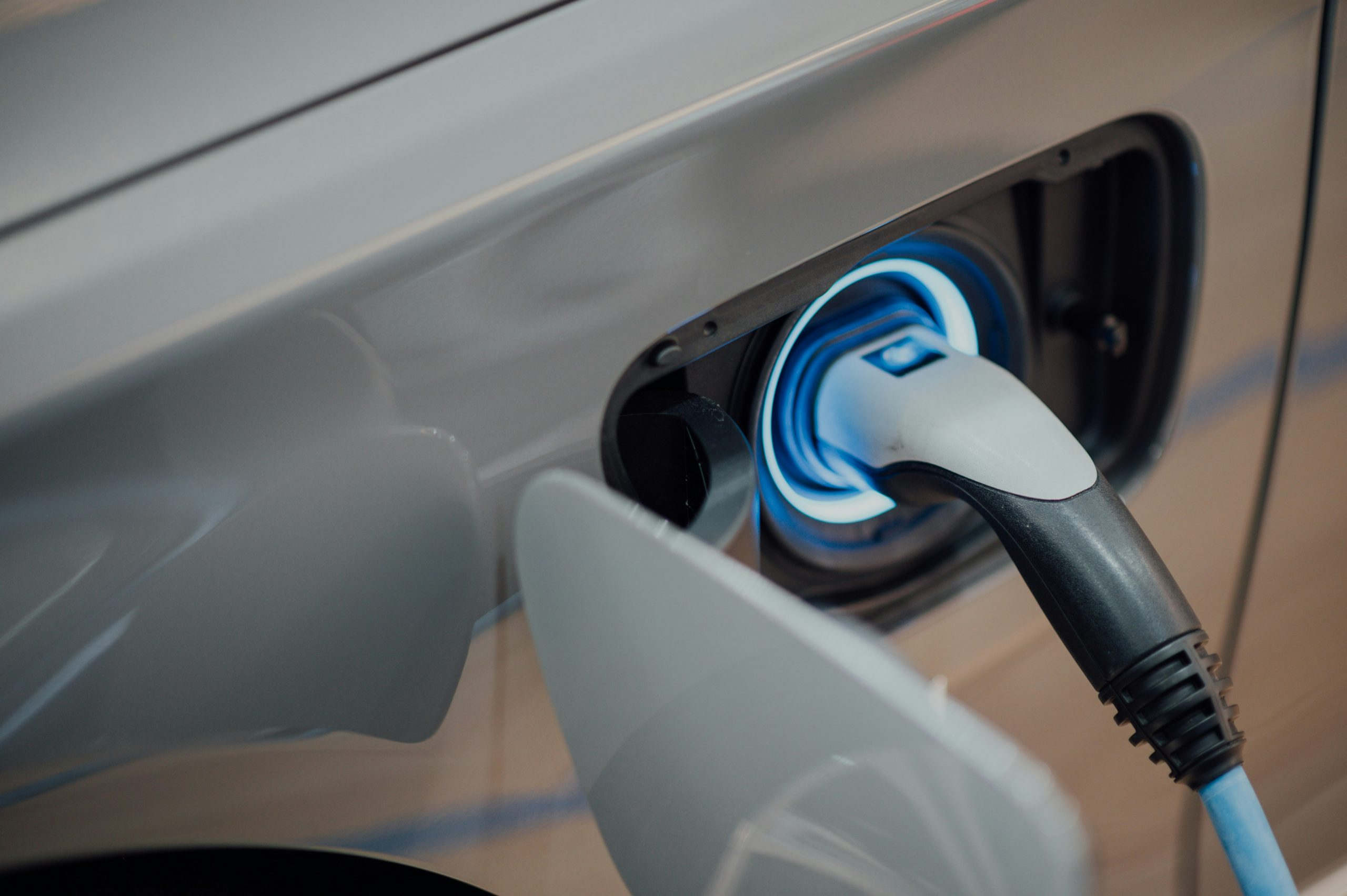
The Current State of Electric Charging Networks
Electric charging networks refer to the infrastructure that supports the charging of all-electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles. These networks consist of charging stations and charging points, which come in various forms, including public charging stations, private home chargers, and fast-charging stations found along highways.
Currently, the electric charging network is dominated by two main types of chargers – Level 2 and DC fast chargers. Level 2 chargers use a 240-volt outlet and can fully charge an electric vehicle in 4-8 hours. On the other hand, DC fast chargers use a higher voltage and can charge an electric car in as little as 30 minutes. However, the biggest challenge lies in the fact that these charging networks are not yet widespread and easily accessible.
Key Challenges Facing Electric Charging Networks
Lack of Uniform Standards
One of the biggest hurdles for electric charging networks is the lack of uniform standards. Currently, there are multiple charging standards, including CHAdeMO, CCS, and Tesla’s Supercharger. This makes it difficult for electric vehicle owners to navigate and utilize different charging networks, especially on long-distance trips.
High Infrastructure Costs
Another major challenge facing electric charging networks is the high infrastructure costs. Building a public charging station or installing a Level 2 charger at home can be quite expensive. These costs are then passed on to the end-user in the form of higher charging fees, deterring potential electric vehicle buyers from making the switch.
Range Anxiety
Range anxiety, or the fear of running out of charge while on the road, is another hurdle for electric charging networks. This is exacerbated by the fact that charging times for Level 2 chargers can take several hours, making long-distance trips time-consuming and inconvenient.
Potential Solutions for a Smooth Transition
Uniform Standards and Interoperability
To mitigate the issue of multiple charging standards, there is a need for standardization and interoperability among charging networks. Efforts are being made to create a common charging standard for all electric vehicles, such as the Combined Charging System (CCS), which can accommodate both Level 2 and DC fast charging.
Investment in Infrastructure
The most significant solution to the lack of charging infrastructure is investment. Governments and private companies must work together to build a robust and extensive network of charging stations to cater to the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. Financial incentives such as tax breaks and subsidies can also help ease the burden for individuals looking to install home charging stations.
Advancements in Technology
The future of electric charging networks looks promising with advancements in technology such as wireless charging and ultra-fast charging. Wireless charging technology eliminates the need for cables and can facilitate seamless charging for electric vehicles while parked. On the other hand, ultra-fast charging, like the upcoming 800-volt charging technology from Porsche, can fully charge an electric vehicle in as little as 15 minutes.
Conclusion
Electric charging networks will play a critical role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As governments and manufacturers pledge to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, investing in robust charging infrastructure is crucial. Further advancements in technology and standardization efforts will also help address key challenges facing electric charging networks, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.